If you want to achieve your goals you need a scale you can trust. Bluetooth Smart Scale that calculates Multi-Frequency Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA) technology is very accurate and useful. Multi-frequency testing provides an additional level of accuracy to the body composition analysis process by providing essential data of a person’s intracellular and extracellular status, and is generally only found on professional grade models. Analysis of the cellular data allows us to determine the quality of the muscle tissue, is addition to mass. A high score represents a higher density of muscle fiber, with less water, fat and connective tissue. A low score indicates the muscle fiber is thinner and fewer compared to other substances.
BIA is quick and non-invasive test simply involves the placement of two electrodes on the person's right hand and right foot. A low level, imperceptible electrical current is sent through the body. The flow of the current is affected by the amount of water in the body. The BIA Scale device measures how this signal is impeded through different types of tissue. Tissues that contain large amounts of fluid and electrolytes, such as blood, have high conductivity, but fat and bone slow the signal down. As BIA determines the resistance to flow of the current as it passes through the body, it provides estimates of body water from which body fat is calculated using selected equations.
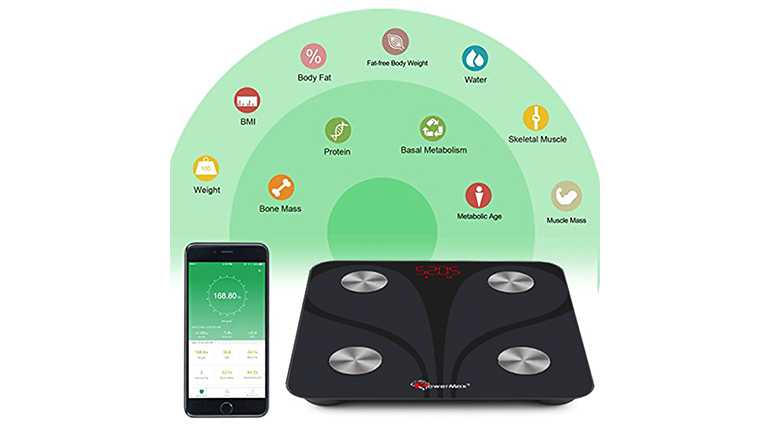
Introducing The PowerMax BCA-130 Bluetooth Smart Scale that calculates Multi-Frequency Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA) technology. The advanced technology found within BCA-130 provides an in-depth analysis of 13 body composition readings. Measurements include: Weight, BMI, Body Fat, Fat-Free Body Weight, Subcutaneous Fat, Visceral Fat, Body Water, Skeletal Muscle, Muscle Mass, Bone Mass, Protein, BMR, and Metabolic Age. No other consumer Bluetooth scale offers such a wide array of capability, making the BCA-130 the world’s best home-use body composition monitor.
The BCA-130 uses Bluetooth technology, monitoring the effectiveness of a weight loss or physical activity program has never been easier. Compatible Android and iOS Smartphone that will record, analyze, and graph your results. It also offers Unlimited users can use same weight scale device, one can store data on cloud and can retrieve it with cloud password if in case you deleted the app or lost your phone, The Application also have password protect feature, Can also share data to your friends and family on social media, Bluetooth scale machine auto – recognize the family members and Application sends you reminder notification to check your weight on regular intervals for your benefits.
Introduction to Body Composition Data and how it works?
Weight- The weight of a body is defined as the force of gravity on the object and can be considered as the mass times the acceleration of gravity.
BMI- BMI means Body Mass Index. A standardized ratio of weight to height used as a general indicator of health. Your BMI can be calculated by dividing your weight (in kilograms) by the square of your height (in meters). BMI is a good general indicator for population studies but has serious limitation when assessing on an individual level.
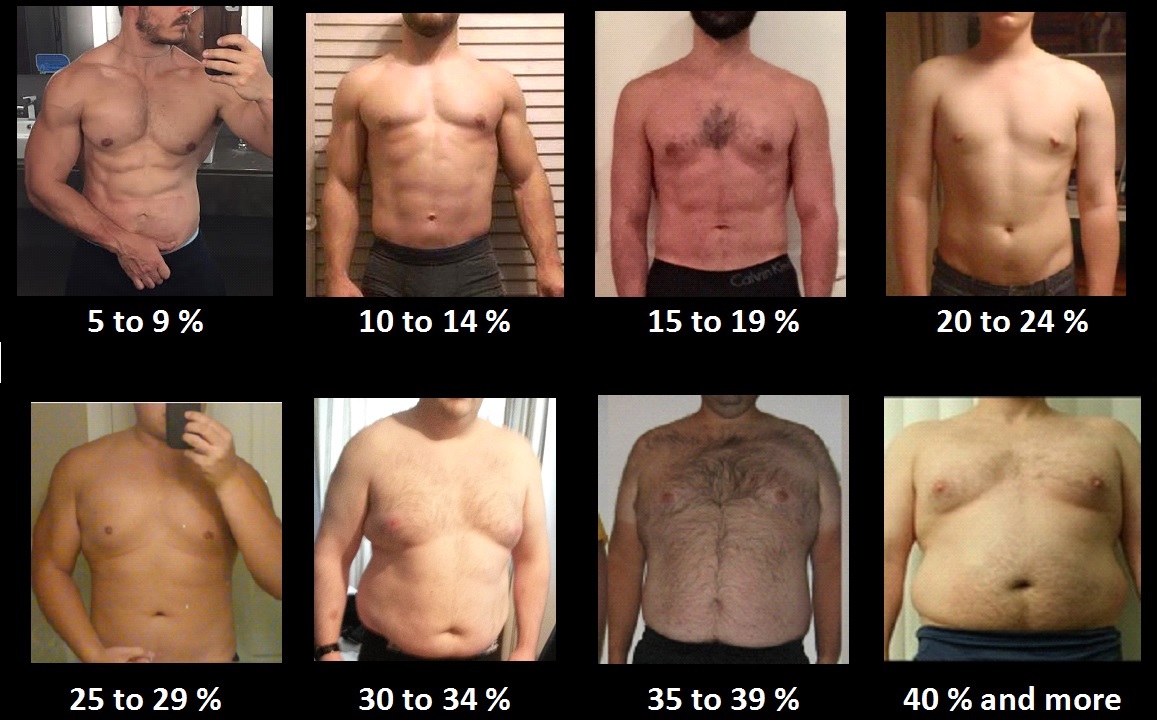
Body Fat- Body Fat Percentage is the proportion of fat to the total body weight. Body Fat Mass is the actual weight of fat in your body. It is essential for maintaining body temperature, cushioning joints and protecting internal organs. The energy, or calories, our body needs comes from what we eat and drink. Energy is burned through physical activity and general bodily functions. If you consume the same number of calories as you burn, all the calories are converted into energy. But if you consume more than you burn, excess calories are stored in fat cells. If this stored fat is not converted into energy later, it creates excess body fat.
Fat-Free Body Weight- Fat-free mass, also known as lean body mass, refers to all of your body components except fat. It includes your body's water, bone, organs and muscle content. However, when it comes to weight management and body composition, fat-free mass refers primarily to muscle mass.
Visceral Fat- Visceral fat is an intra-abdominal fat, which is stored around and between your organs in your abdomen. Even if your weight and body fat remains constant, as you get older the distribution of fat changes and is more likely to shift to the abdominal area. Ensuring you have a healthy level of visceral fat directly reduces the risk of certain diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure and diabetes.
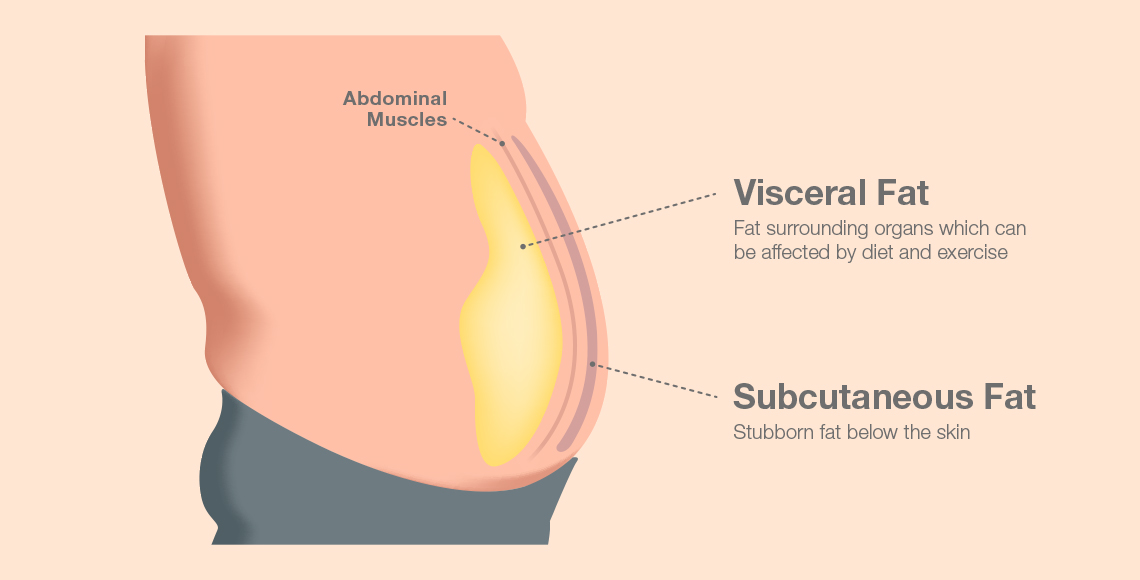
Subcutaneous Fat- The subcutaneous fat under your skin is just one type of stored fat in your body. Because subcutaneous fat lies right under your skin, it can be measured using bioelectrical impedance on several parts of your body, which might include your abdomen, sides, chest, the back of your arms and the front of your thighs.
Body Water- body water is the water content of a body that is contained in the tissues, the blood, the bones and elsewhere. The hydration level is measured by using the Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA). The same analysis that is used to calculate your body fat is used to calculate your hydration level. Taking into consideration a user's age and gender, a calculation is made that determines the percentage of water.
Skeletal Muscle- Skeletal muscle, also called voluntary muscle, invertebrates, most common of the three types of muscle in the body. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons, and they produce all the movements of body parts in relation to each other. Unlike smooth muscle and cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle is under voluntary control.
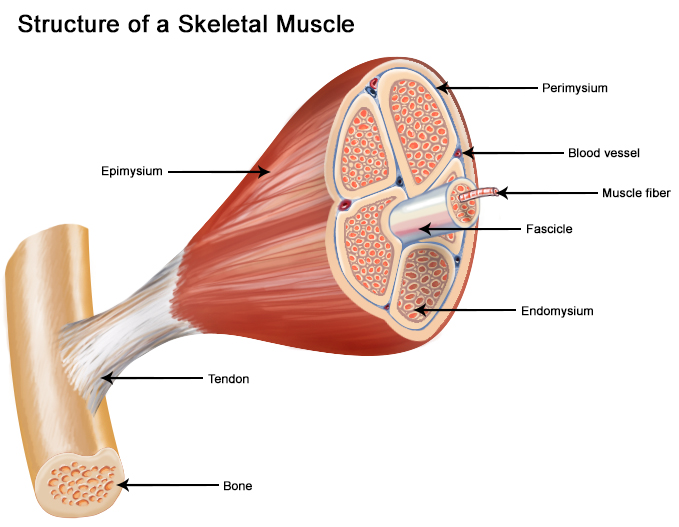
Muscle Mass- Muscle mass is the physical size of the muscle; muscles are often large due to exercise and concentrated physical training, but not exclusively. "Bioelectrical impedance analysis" has been added to traditional bathroom scales. The scales send a harmless electrical current up through your body to read the amount of fat body mass and lean body mass --calculating your percentage of body fat.
Bone Mass- Bone is a living, growing tissue. When you are young, your body makes new bone tissue faster than it breaks down older bone. In young adulthood, bone mass is at its peak; after that, bone loss starts to outpace bone growth, and bone mass decreases. The predicted weight of bone mineral in your body. While your bone mass is unlikely to undergo noticeable changes in the short term, it’s important to maintain healthy bones by having a balanced diet rich in calcium and by doing plenty of weight-bearing exercise. You should track your bone mass over time and look for any long term changes.
Protein- Proteins are one of the four different types of macromolecules, in addition to carbohydrates, lipids, or fats, and nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA. It is a macronutrient that is essential to building muscle mass. The electrical current flows more quickly through water and muscle than bone or fat, the scale measures the speed of the current.
BMR- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is an estimation of the energy (measured in calories) expended by the body, at rest, to maintain normal body functions. This continual work makes up about 60-70% of the calories the body uses and includes the beating of your heart, respiration, and the maintenance of body temperature. Your BMR is influenced by a number of factors, including age, weight, height, gender, dieting and exercise habits.
Metabolic Age- Metabolic age is a comparison between a person's basal metabolic rate (BMR) against the average BMR for an age. The Metabolic age is calculated by comparing your Basal Metabolic Rate to the average BMR of your chronological age group. If your metabolic age is higher than your actual age, it's a sign that you need to improve your metabolic rate.
 India (INR)
India (INR)
 UAE (AED)
UAE (AED)
 Store Locator
Store Locator





-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)
-thumb.jpg)